Look at the above picture. Saigo-san, why are you weeping? It shows a bronze statue of Japanese warrior Takamori Saigo (1827-77) in Tokyo's Ueno Park. It looks as though he is crying. Wonder why?
To understand about acid rain, you have to have a basic understanding of pH. pH is use to denote the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+ ) in solution. The pH factor, is a readable introduction into the topic. pH ranges from 0 (zero) to 14. The lower the pH (the higher the concentration of hydrogen ions), the more acidic the solution. pH Table illustrates the scale with examples of substances and their pH's. Bear in mind that going from pH 2 to pH 1 represents a 10-fold increase in hydrogen ions. A substance with pH 1 has 10 times the amount of hydrogen ions as a substance with pH 2. Another site, which gives essentially the same information is The pH Scale. If you want to delve more deeply into the topic of pH, look at The pH-Acid/Base Tutorial.
Acid rain is a term one hears often, but what exactly is acid rain? British Chemist Robert Angus Smith first used the term "acid rain" in 1872 in a book entitled Acid Rain: The Beginnings of a Chemical Climatology. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's web site explains that a better term would be acid deposition-the return to earth of acid pollutants in the atmosphere by either wet or dry means. Wet deposition is sometimes termed acid precipitation (rain, hail, fog or snow with a pH value of less than 5.6). Dry deposition is acidic gases and particles falling back to earth.
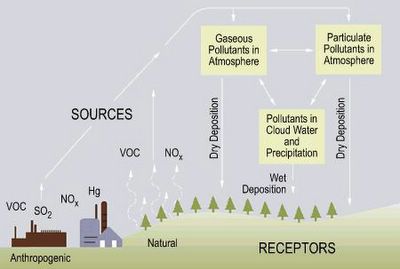
Origins of acid rain.

So what causes acid rain? Simply put, acid rain is cause by human activity and sulfur and nitrogen are the two elements mainly responsible for the harmful effects. Take a look at the web site acid rain. Unpolluted rainwater is slightly acidic due to the presence of dissolved CO2 (carbon dioxide), NO (nitric oxide), and SO2 (sulfur dioxide), which occur naturally in the atmosphere. However, it is NO and S02 from anthropogenic or human made sources that cause the problem. Car exhaust and the burning of fossil fuels adds greatly to the amount of NO and SO2 in the atmosphere thus decreasing the pH (or increasing the acidity) of rainwater.
Is acid rain a problem? The effects of acid rain can be seen on our lakes and streams (or lake, rivers and streams), forests (or forests), building, monuments, tombstones, bridges and statues and even our health.
Is there anything that you can do to reduce acid rain emissions? Environmental Canada web site has some suggestions.